Functional Recovery
Functional recovery is an approach designed to reintegrate individuals into their daily activities, whether they are related to sports or non-sports. An essential aspect of this program is replicating the specific conditions encountered by each individual during their daily routines. This holds dual importance as it provides the physiotherapist with valuable information about the person’s condition while also offering feedback to the individual. It is crucial to note that active participation is emphasized, making the person an integral part of the rehabilitation process.

Pressure Cryotherapy
During the acute stage of musculoskeletal injuries, inflammation and swelling occur in the affected area. As a result, certain physical therapy modalities become contraindicated. However, applying cold therapy and gentle pressure to the area can effectively alleviate swelling and inflammation, especially when combined with a cryotherapy/pressotherapy device. Swiftly addressing swelling and inflammation significantly contributes to reducing recovery time.

T.E.C.A.R. therapy
T.E.C.A.R. therapy, an advanced form of diathermy, has emerged as a leading technique in the field of physical therapy in recent years. Ongoing research continues to provide new insights into its effectiveness in managing chronic musculoskeletal conditions. This therapy exhibits analgesic properties and is considered highly safe for use.
Percussive Ultrasound
Specific musculoskeletal conditions, such as elbow epicondylitis (tennis elbow), plantar fasciitis, and calcifying tendinitis, require targeted rehabilitation and specialized equipment. Research has demonstrated that incorporating impact ultrasound into the treatment of these conditions yields promising results and significantly reduces recovery time.
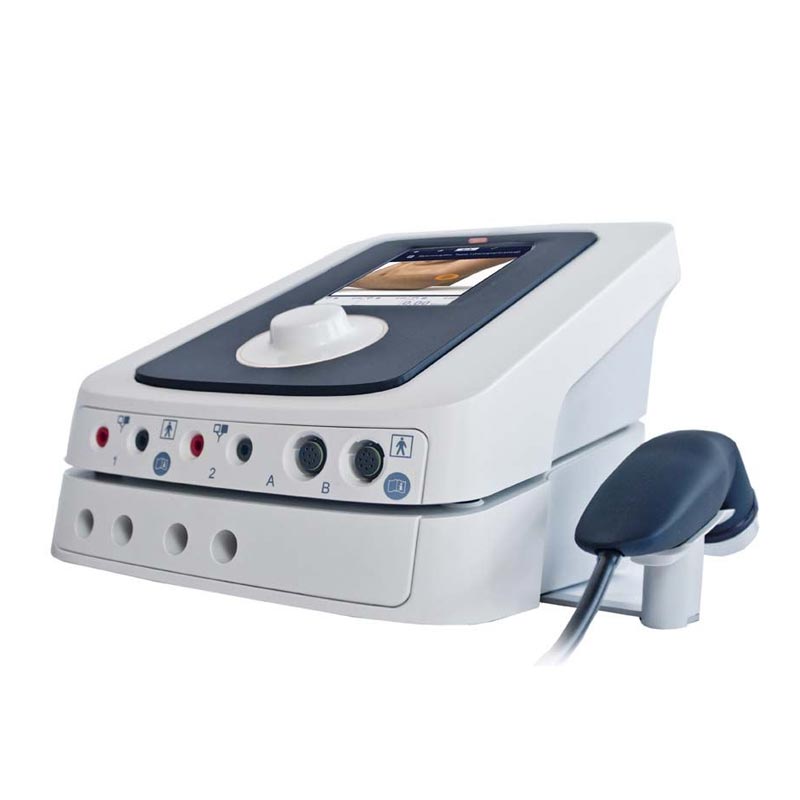
Electrotherapy and Ultrasound
Electrotherapy and ultrasound are two of the most basic weapons in a physical therapist’s quiver as they are used daily in a wide range of situations. There are many therapeutic effects from its use, the most important being, analgesia, anti-inflammatory action, hyperemia and increasing the elasticity of connective tissues and collagen.